CSS 定位机制
CSS 有三种基本的定位机制:普通流、浮动和绝对定位。
position 属性
-
static—— 元素框正常生成。块级元素生成一个矩形框,作为文档流的一部分,行内元素则会创建一个或多个行框,置于其父元素中。
-
relative—— 元素框偏移某个距离。元素仍保持其未定位前的形状,它原本所占的空间仍保留。是相对之前正常位置的变化。
-
absolute—— 元素框从文档流完全删除,并相对于其包含块定位。包含块可能是文档中的另一个元素或者是初始包含块。元素原先在正常文档流中所占的空间会关闭,就好像元素原来不存在一样。元素定位后生成一个块级框,而不论原来它在正常流中生成何种类型的框。
-
fixed—— 元素框的表现类似于将 position 设置为 absolute,不过其包含块是视窗本身。

CSS 浮动——demo
通过 float 属性实现元素的浮动。

使用clear 属性,使图像的左侧和右侧均不允许出现浮动元素:
1
2
3
4
5
img
{
float:left;
clear:both;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
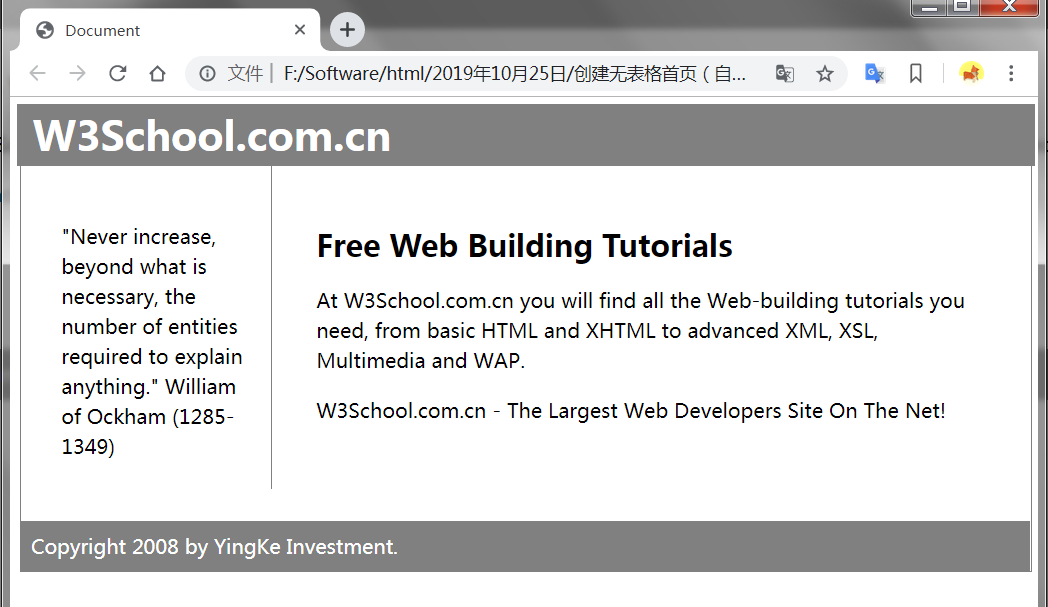
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
#all {
border: 1px solid gray;
line-height: 150%;
width: 100%;
}
.header,
.footer {
background-color: gray;
color: white;
padding: 0.4em;
clear: both;
}
h1.header {
margin: -10px;
}
p.footer {
margin: -5px;
}
.left {
float: left;
width: 150px;
padding: 2em;
}
.txt {
margin-left: 200px;
border-left: 1px solid gray;
padding: 35px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="all">
<div class="header">
<h1 class="header">W3School.com.cn</h1>
</div>
<div>
<p class="left">"Never increase, beyond what is necessary, the number of entities required to explain
anything." William
of Ockham (1285-1349)</p>
</div>
<div class="txt">
<h2>Free Web Building Tutorials</h2>
<p>At W3School.com.cn you will find all the Web-building tutorials you need, from basic HTML and XHTML to
advanced XML, XSL, Multimedia and WAP.</p>
<p>W3School.com.cn - The Largest Web Developers Site On The Net!</p>
</div>
<div class="footer">
<p class="footer">Copyright 2008 by YingKe Investment.</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>